System

Survey

Transfer

Design

Calibration

Reserve
Leveling for the Next-level Yield
Leveling for the Next-level Yield
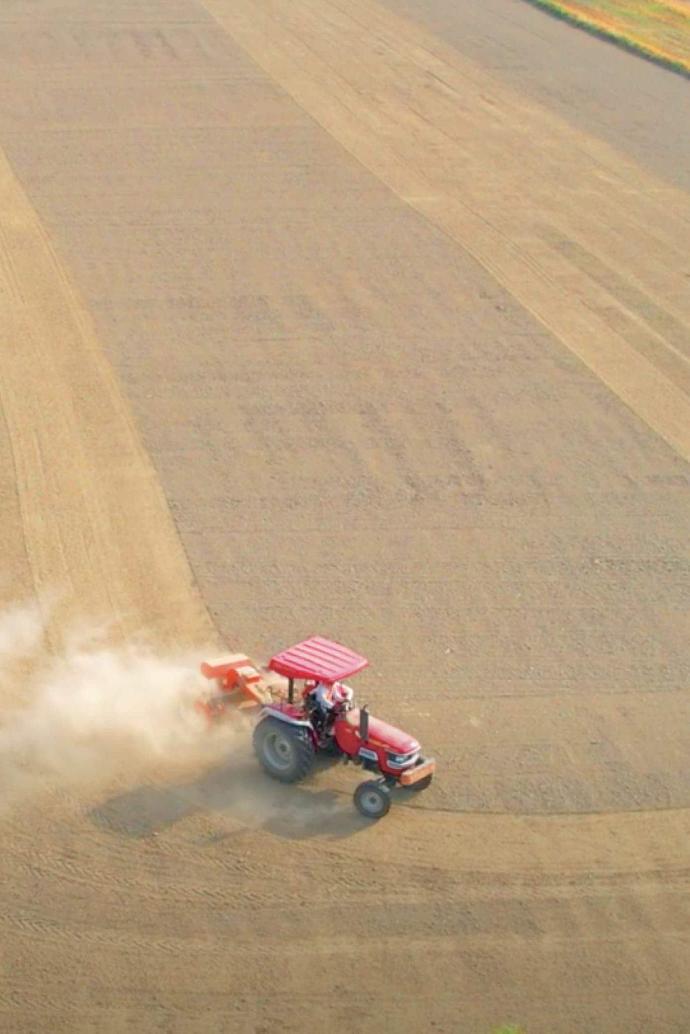
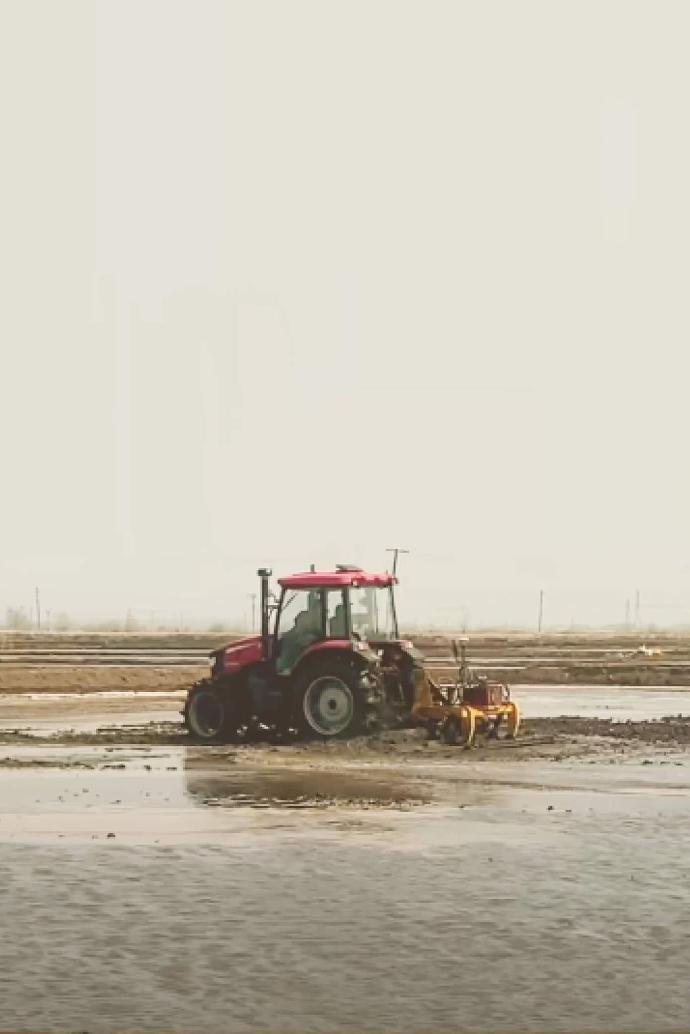
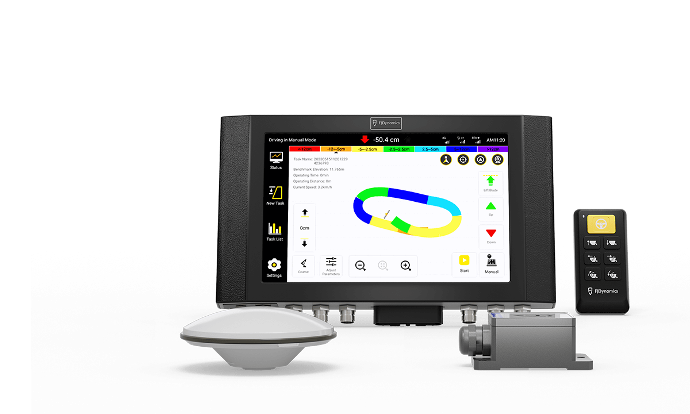
GNSS-based Land Leveling System
Streamlined Project Design
Terrain Survey
Terrain Design
Record Reserve
Application Scenarios
Benefits
Benefits

Work Efficiency

Fuel Consumption

Water Consumption
 40%
40%
Work Efficiency
 10%
10%
Fuel Consumption
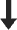 22%
22%
Water Consumption